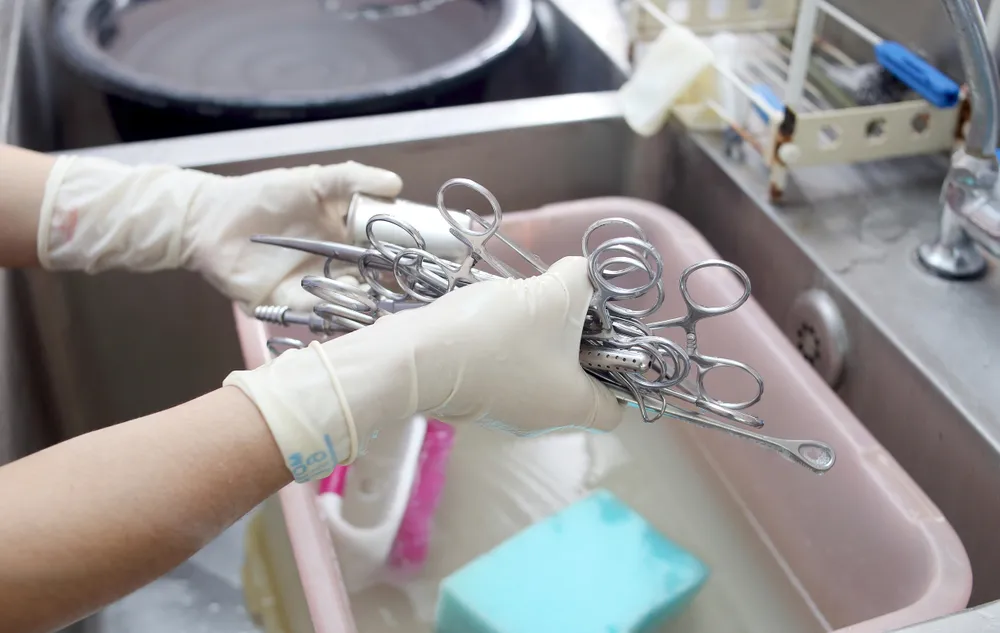
How to save a tool after use
Proper maintenance and storage of tools after use are crucial for ensuring their longevity, performance, and safety. Whether you’re handling surgical instruments, veterinary tools, or farrier equipment, following the right steps can significantly extend their lifespan and keep them in optimal condition. Here’s a guide on how to save your tools after use.
1. Immediate Cleaning and Sanitization
After each use, the first step is to clean your tools immediately. This is especially important for surgical and veterinary instruments, where any residue or biological material left behind can lead to corrosion or contamination. Use appropriate cleaning agents and follow manufacturer guidelines to ensure thorough cleaning without damaging the tools.
2. Drying Tools Thoroughly
Moisture is one of the biggest enemies of metal tools. After cleaning, make sure your tools are completely dry before storing them. For surgical instruments, use a lint-free cloth or an air dryer to remove all moisture. For farrier and equestrian tools, ensure they are wiped down and left to air dry in a clean environment.
3. Inspecting for Damage
Regular inspection is key to maintaining tool quality. After cleaning and drying, carefully inspect each tool for any signs of wear, damage, or corrosion. If any issues are found, address them immediately to prevent further degradation. This step is critical for tools that require precision, such as surgical instruments and hoof care tools.
4. Proper Lubrication
For tools with moving parts, such as pliers, clippers, or ratchets, applying a light coat of lubricant can prevent rust and ensure smooth operation. Choose a lubricant that is safe and recommended for the specific material of your tools. Surgical and veterinary instruments may require specialized lubricants that are safe for medical use.
5. Storing in a Safe Environment
Storing your tools correctly is as important as cleaning them. Use a tool chest, drawer, or storage case that protects them from dust, moisture, and environmental factors. For surgical and veterinary tools, consider using sterilized packaging or pouches that maintain sterility until the next use. Farrier tools and other heavy-duty equipment should be stored in a cool, dry place where they won’t be exposed to humidity or extreme temperatures.
Check for Wear and Tear
Before storing your tool, give it a quick inspection. Look for any signs of damage, loose parts, or wear and tear. Identifying issues early can save you from costly repairs down the line.
6. Regular Maintenance Schedule
Establishing a regular maintenance schedule can help keep your tools in top shape. This includes routine cleaning, lubrication, and inspection. For professional use, such as in a medical or veterinary setting, this schedule should be strictly adhered to, ensuring that every tool is always ready for its next use.
7. Replacing Worn Tools
No tool lasts forever. Recognizing when a tool has reached the end of its useful life is crucial. If a tool is showing signs of significant wear, corrosion, or damage that cannot be repaired, it’s time to replace it. Continuing to use a compromised tool can lead to subpar performance and even safety risks.
Conclusion Saving and maintaining your tools properly after each use is an investment in their longevity and effectiveness. By following these steps, you can ensure that your tools remain reliable and ready for use, whether you’re in a surgical theater, a veterinary clinic, or out in the field.
Related Posts
At EPISURG, we believe in making every step of your journey with us a smooth one, starting with your...
read more
10
Mar
Return & Replacement
At EPISURG, we’re committed to making your experience with our products seamless from start to finish. If you ever need...
read more


